Below are listed some of the supplements that have significantly demonstrated efficacy in potentiating the ability of very high-dose intravenous vitamin C to kill cancer (40g/hr. +/-20g, for 1-3 hours). It is expected that they will also have the same potentiating effect with the SuCCeED IVC Protocol.
-
- Alpha Lipoic Acid1
- Vitamin E 2
- Vitamin K3 if possible (Apatonetm)1,3, otherwise do take Vitamin K1 or K2 4
- Lecithin5
- Artemisinin if possible6
- Dfraction (Maitake mushroom) supplement if possible7
- DCA (dichloroacetate)8
- Quercetin3
- Curcumin3
- Do with other oxidative therapies. Hypoxia at the cancer site is likely the #1 reason when treatment efficacy falls short of in vitro success. Here’s how to mitigate that:
- O2 Mask
- Ozone generator in the room
- Hyperbaric Oxygen
- DCA (dichloroacetate) administration
- Exercise Bike, increases blood flow to tumor and oxygenation
- Do reasonable Conventional Chemotherapy
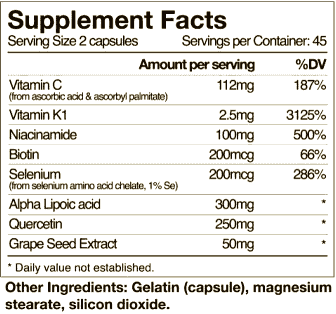
Note some of these are available in a combined supplement called IVC Max (by Aidan Products, associated with the Riordan Clinic). This is easily found with a websearch. It contains many of the supplements mentioned herein specifically for the purpose of potentiating IVC. The ingredients as of this published date as shown in this nutrition fact label shown here.
It is mentioned here as definitely being beneficial because of the Vitamin K1, ALA, and Quercetin, which is convenient to have in one supplement. The additional ingredients should have a possible to likely effect in improving efficacy.
References
- JJ Casciari, NH Riordan, TL Schmidt, XL Meng, JA Jackson, and HD Riordan; Cytotoxicity of
ascorbate, lipoic acid, and other antioxidants in hollow fibre in vitro tumours; British Journal of
Cancer (2001) 84(11), 1544–1550 doi: 10.1054/ bjoc.2001.1814,;
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2363673 - Tomasetti M, Strafella E, Staffolani S, Santarelli L, Neuzil J, Guerrieri R.; alphaTocopheryl
succinate promotes selective cell death induced by vitamin K3 in combination with ascorbate.; Br
J Cancer. 2010 Apr 13;102(8):122434. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6605617. Epub 2010 Mar 23.;
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20332775 - Lamson DW, Gu YH, Plaza SM, Brignall MS, Brinton CA, Sadlon AE.; The vitamin C:vitamin K3
system enhancers and inhibitors of the anticancer effect.; Altern Med Rev. 2010
Dec;15(4):34551.; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21194250 - Verrax J, Taper H, Buc Calderon P.; Targeting cancer cells by an oxidantbased therapy.; Curr Mol
Pharmacol. 2008 Jan;1(1):8092.; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/20021426 - Pancorbo D, Vazquez C, Fletcher MA.; Vitamin Clipid metabolites: uptake and retention and
effect on plasma Creactive protein and oxidized LDL levels in healthy volunteers.; Med Sci Monit.
2008 Nov;14(11):CR54751.; http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18971870 - Efferth T.; Molecular pharmacology and pharmacogenomics of artemisinin and its derivatives in
cancer cells.; Curr Drug Targets. 2006 Apr;7(4):40721.;
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16611029 - Alexander B1, Fishman AI, Eshghi M, Choudhury M, Konno S.; Induction of cell death in renal cell
carcinoma with combination of Dfraction and vitamin C.; Integr Cancer Ther. 2013
Sep;12(5):4428. doi: 10.1177/1534735412473643. Epub 2013 Jan 22.;
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23341484 - Akbar Khan, MD; Denis Marier, ND; Eric Marsden, ND; Douglas Andrews, ND; Isaac Eliaz, MD; A
Novel Form of Dichloroacetate Therapy for Patients With Advanced Cancer: A Report of 3 Cases;
ALTERNATIVE THERAPIES, VOL. 20, SUPPL. 2 27
http://alternativetherapies.com/at/web_pdfs/s202khan.pdf
